David Ronca has had a long history in the industry and is most known for his time at Netflix where he was pivotal in the inception and implementation of many technologies. Because Netflix was one of the first companies streaming video on the internet, and at a global scale, they are responsible for many innovations that the industry as a whole benefits from today and are the recipient of 7 technical Emmys. David is often pictured holding an Emmy awarded to Netflix for their role in the standardisation and promotion of Japanese subtitles one of the less-talked-about innovations in contrast to VMAF, Per-Title encoding and per-shot encoding.
In this video, talking to John Porterfield, David talks about the early days at Netflix when it was pivoting from emailing DVDs to streaming. He talks about the move from Windows-based applications to cross-platform technologies, at the time Microsoft Silverlight which was a big direction shift for Netflix and for him. The first Silverlight implementation within Netflix was also the first adaptive bitrate (ABR) version of Netflix which is where David found he next calling within Netflix writing code to synchronise the segments after DRM.
The PS3, David recalls, was the worlds most powerful Blu-ray player and part of the Blu-ray spec is a Java implementation. David recounts the six months he spent in a team of three working to implement a full adaptive bitrate streaming application within Blu-ray’s Java implementation. This was done in order to get around some contractual issues and worked by extending the features which were built into Blu-ray for downloading new trailers to show instead of those on disc. This YouTube review from 2009 shows a slick interface slowed down by the speed of the internet connection.
David also talks about his close work with and respect for Netflix colleague Anne Aaron who has been featured previously on The Broadcast Knowledge. He goes on to talk about the inception of VMAF which is a metric for computationally determining the quality of video developed by Netflix as they didn’t feel that any of the current metrics such as PSRN and MS-SSIM captured the human opinion of video well enough. It’s widely understood that PSNR has its place but can give very different results to subjective evaluations. And, indeed, VMAF also is not perfect as David mentions. However, using VMAF well and understanding its limits results in a much more accurate description of quality than with many other metrics and unlike competing metrics such as SSIMWAVE’s SSIMPLUS, is open source and royalty-free.
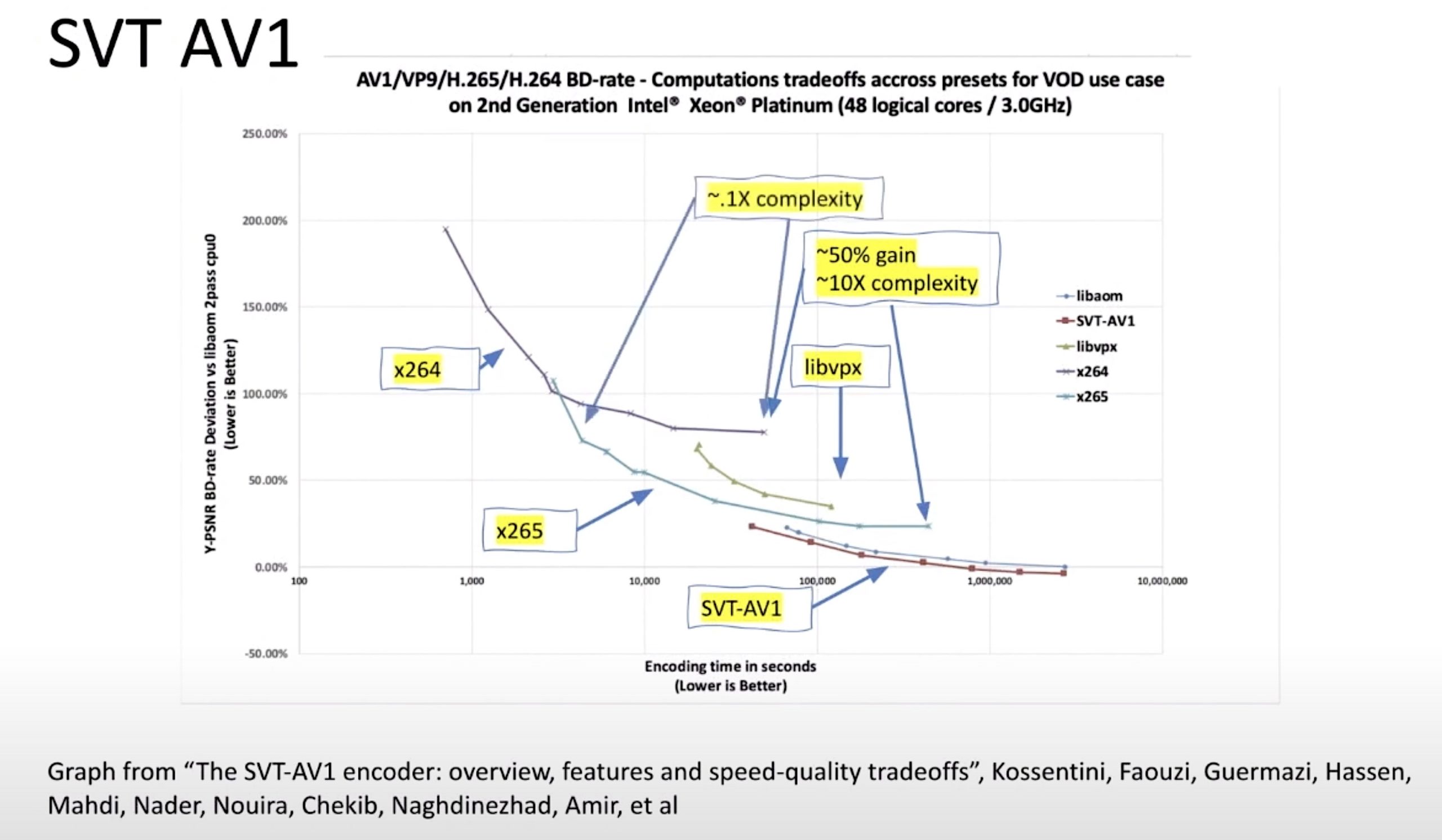
David concludes his talk with John saying that high-quality, well-delivered streaming is now everywhere. The struggles of the early years have resulted in a lot of well-learned lessons by the industry at large. This commoditisation is welcome and shows a maturity in the industry that begs the question about where the puck is going to next. For David, he sees environmental sustainability to be one of the key goals. Both environmentally and financially, he says that streaming providers will now want to maximise the output-per-watt of their data centres. Data centre power is currently 3% of all global power consumption and is forecast to reach up to 20%. Looking to newer codecs is one way to achieve a reduction in power consumption. David spoke about AV1 last time he spoke with John which delivers lower bitrate with high computation requirements. At hyperscale, using dedicated ASIC chips to do the encoding is one way to drive down power consumption. An alternative route is new MPEG codec LCEVC which delivers better-than-AVC performance in software at much-reduced power consumption. With the prevalence of video – both for entertainment and outside, for example, body cams – moving to more power-efficient codecs and codec implementations seems the obvious and moral move.
Watch now!
Speakers
 |
David Ronca Director, Video Encoding, |
 |
Freelance Video Webcast Producer and Tech Evangelist JP’sChalkTalks YouTube Channel |