Today’s video has a wide array of salient topics from seven speakers at SMPTE Toronto’s meeting in February. Covering Uncompressed IP networking, colour theory & practice, real-time virtual studios and AI, those of us outside of Toronto can be thankful it was recorded.
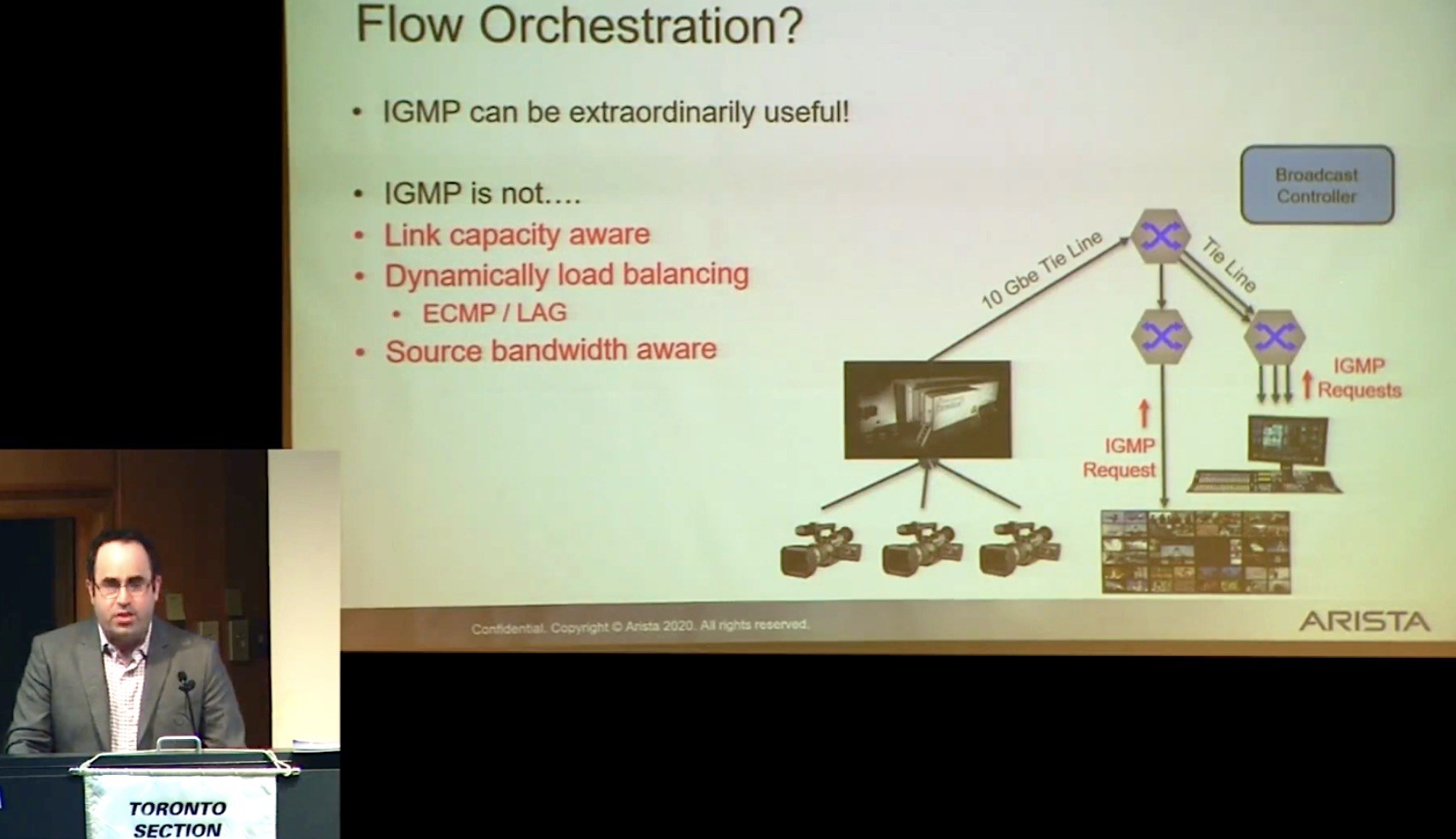
Ryan Morris from Arista (starting 22m 20s) is the first guest speaker and kicks off with though-provoker: showing the uncompressed bandwidths of video, we see that even 8K video at 43Gb/s is much lower than the high-end network bandwidths available in 400Gbps switch ports available today with 800Gbps arriving within a couple of years. That being said, he gives us an introduction to two of the fundamental technologies enabling the uncompressed IP video production: Multicast and Software-Defined Networking (SDN).
Multicast, Ryan explains is the system of efficiently distributing data from one source to many receivers. It allows a sender to only send out one stream even if there are a thousand receivers on the network; the network will split the feed at the nearest common point to the decoder. This is all worked out using the Internet Group Message Protocol (IGMP) which is commonly found in two versions, 2 and 3. IGMP enables routers to find out which devices are interested in which senders and allows devices to register their interest. This is all expressed by the notion of joining or leaving a multicast group. Each multicast group is assigned an IP address reserved by international agreement for this purpose, for instance, 239.100.200.1 is one such address.
Ryan then explores some of the pros and cons of IGMP. Like most network protocols each element of the network makes its own decision based on standardised rules. Though this works well for autonomy, it means that there no knowledge of the whole system. It can’t take notice of link capacity, it doesn’t know the source bandwidth, you can guess where media will flow, but it’s not deterministic. Broadcasters need more assurance of traffic flows for proper capacity planning, planned maintenance and post-incident root cause analysis.
SDN is an answer to this problem. Replacing much of IGMP, SDN takes this micro-decision making away from the switch architecture and replaces it with decisions made looking at the whole picture. It also brings an in important abstraction layer back to broadcast networks; engineers are used to seeing X-Y panels and, in an emergency, it’s this simplicity which gets things back on air quickly and effectively. With SDN doing the thinking, it’s a lot more practical to program a panel with human names like ‘Camera 1’ and allow a take button to connect it to a destination.
Next is Peter Armstrong from THP who talks about colour in television (starting 40m 40s). Starting back with NTSC, Peter shows the different colour spaces available from analogue through to SD then HD with Rec 709 and now to 3 newer spaces. For archiving, there is an XYZ colour space for archival which can represent any colour humans can see. For digital cinema there is DCI-P3 and with UHD comes BT 2020. These latter colour spaces provide for display of many more colours adding to the idea of ‘better pixels’ – improving images through improving the pixels rather than just adding more.
Another ‘better pixels’ idea is HDR. Whilst BT 2020 is about Wide Colour Gamut (WCG), HDR increases the dynamic range so that the brightness of each pixel can represent a brightness between 0 and 1000 NITs, say instead of the current standard of 0 to 100. Peter outlines the HLG and PQ standards for delivering HDR. If you’re interested in a deeper dive, check out our library of articles and videos such as this talk from Amazon Prime Video. or this from SARNOFF’s Norm Hurst.
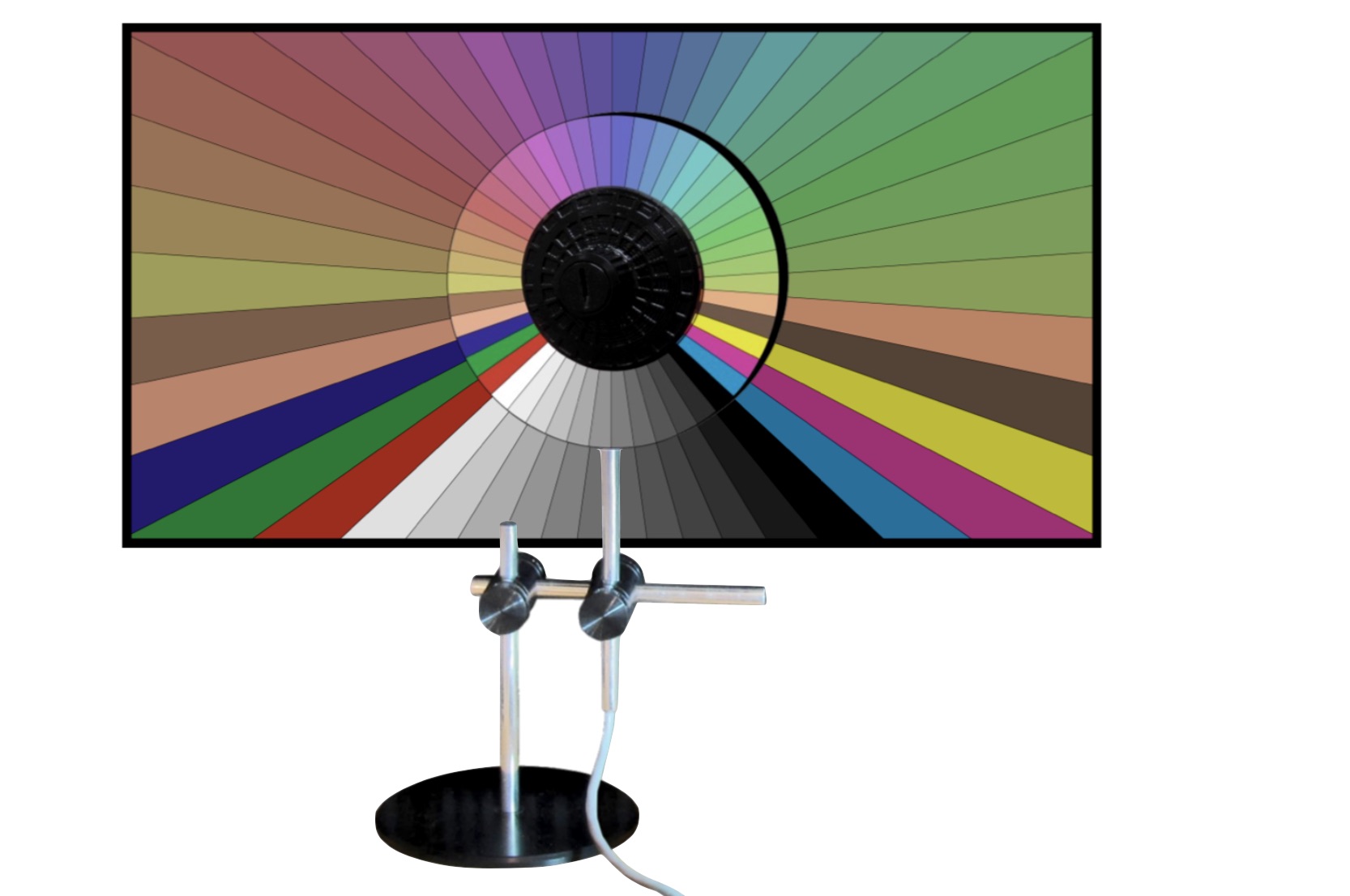
SMPTE fellow and founder of DSC Laboratories, David Corley (56m 50s), continues the colour theme taking us on an enjoyable history of colour charting over the past 60 years up to the modern day. David explains how he created a colour chart in the beginning when labs were struggling to get colours correct for their non-black and white film stock. We see how that has developed over the years being standardised in SMPTE. Recently, he explains, they have a new test card for digital workflows where the camera shoots a special test card which you also have in a digital format. In your editing suite, if you overlay that file on the video, you can colour correct the video to match. Furthermore, DSC have developed a physical overlay for your monitor which self-illuminates meaning when you put it in front of your monitor, you can adjust the colour of the display to match what you see on the chart in front.
Gloria Lee (78m 8s) works for Graymeta, a company whose products are based on AI and machine learning. She sets the scene explaining how broadly our lives are already supported by AI but in broadcast highlights the benefits as automating repetitive tasks, increasing monetisation possibilities, allowing real-time facial recognition and creating additional marketing opportunities. Gloria concludes giving examples of each.
Cliff Lavalée talks about ‘content creation with gaming tools’ (91m 10s) explaining the virtual studio they have created at Groupe Média TFO. He explains the cameras the tracking and telemetry (zoom etc.) needed to ensure that 3 cameras can be moved around in real-time allowing the graphics to follow with the correct perspective shifts. Cliff talks about the pros and cons of the space. With hardware limiting the software capabilities and the need for everything to stick to 60fps, he finds that the benefits which include cost, design freedom and real-time rendering create an over-all positive. This section finishes with a talk from one of the 3D interactive set designers who talks us through the work he’s done in the studio.
Mary Ellen Carlyle concludes the evening talking about remote production and esports. She sets the scene pointing to a ‘shifting landscape’ with people moving away from linear TV to online streaming. Mary discusses the streaming market as a whole talking about Disney+ and other competitors currently jostling for position. Re-prising Gloria’s position on AI, Mary next looks further into the future for AI floating the idea of AI directing of football matches, creating highlights packages, generating stats about the game, spotting ad insertion opportunities and more.
Famously, Netlflix has said that Fortnite is one of its main competitors. And indeed, esports is a major industry unto itself so whether watching or playing games, there is plenty of opportunity to displace Netflix. Deloitte Insights claim 40% of gamers watch esports events at least once a week and in terms of media rights, these are already in the 10s and 100s of millions and are likely to continue to grow. Mary concludes by looking at the sports rights changing hands over the next few years. The thrust being that there are several high profile rights auctions coming up and there is likely to be fervent competition which will increase prices. Some are likely to be taken, at least in part, by tech giants. We have already seen Amazon acquiring rights to some major sports rights.
Watch now!
Speakers
 |
Ryan Morris Systems Engineer, Arista |
 |
Gloria Lee VP, Business Development Graymeta Inc. |
 |
Mary Ellen Carlyle SVP & General Manager, Dome Productions |
 |
Cliff Lavalée Director of LUV studio services, Groupe Média TFO |
 |
Peter Armstrong Video Production & Post Production Manager, THP |
 |
David Corley Presiedent, DSC Labs |