As the amount of video consumed on the internet continues to grow, technologies that unify over-the-air broadcast with internet delivery. Doing this should allow a seamless mix meaning viewers can choose a service without knowing how it’s arriving at their TV, mobile device or laptop. This is the principle behind DVB-I and HbbTV.
In this webinar, Peter MacAvock and Peter Lanigan join moderator
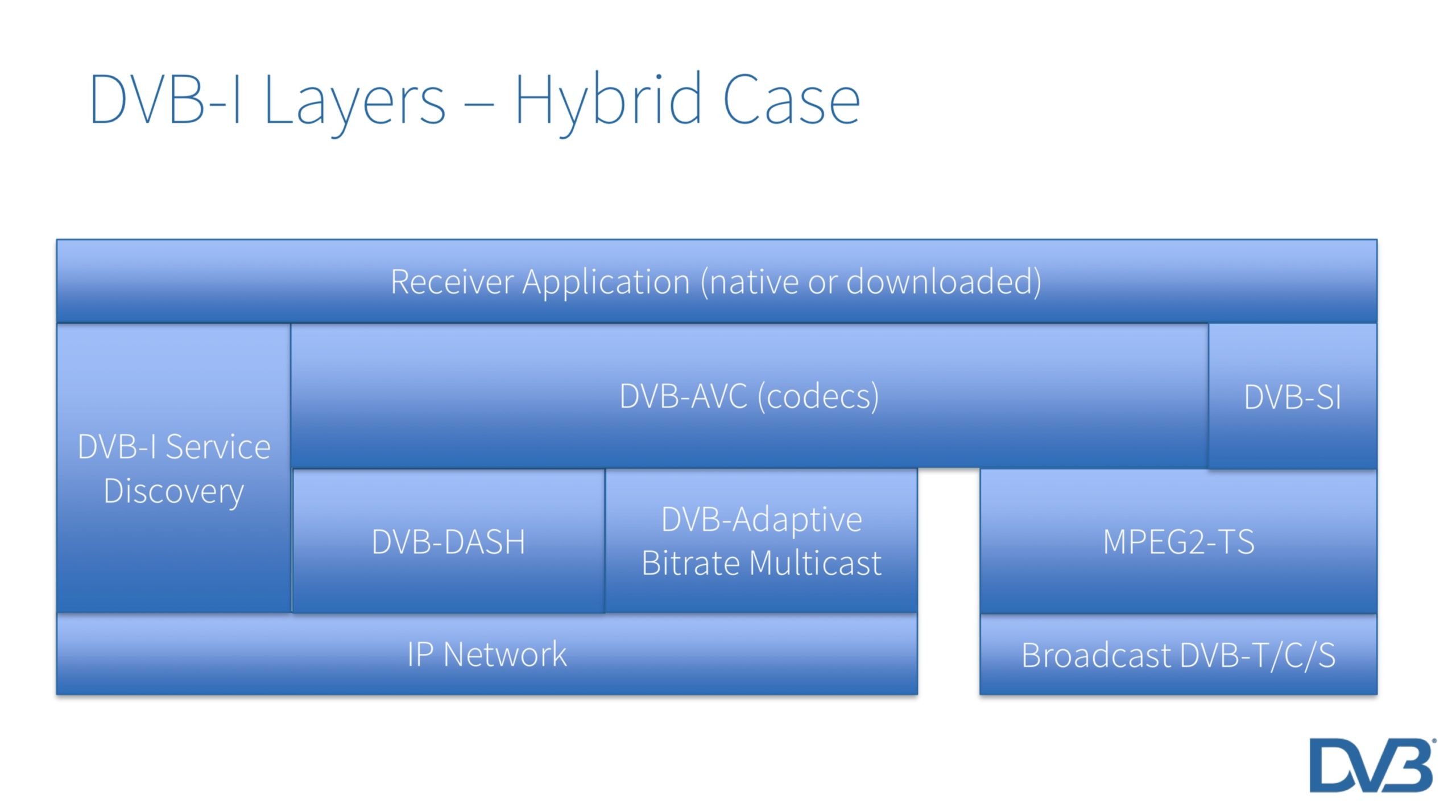
Famous for the widespread technologies of DVB-T, -S and -C which underpin much of the world’s broadcasting, DVB have recently developed a broadcast-focused version of MPEG DASH called DVB-DASH on which DVB-I is built. Where there -T in DVB-T is for terrestrial broadcast and the -S in DVB-S for satellite broadcast, the -I in DVB-I stands for internet. Built upon the DVB-DASH standard DVB-I delivers services over the Internet to devices with broadband access whether that’s raw internet or over operator-managed networks. Most importantly, this isn’t just about TVs, but any device.
DVB-I aims to offer a way unify over-the-air broadcast with internet delivery. The apps used to deliver services to smartphones, tablets and desktops tend to create segregation as each provider delivers their own app. However, there is a benefit to removing the need for each broadcaster needing to maintain their app on all the many platforms. By unifying delivery, DVB-I also makes life easier for manufacturers who can deliver a single, consistent experience. Finally, it opens up a market for more general apps which deliver a TV experience without being tied to one broadcaster opening up more business models and a route to independent innovation.
‘Service Lists’ are the fundamental currency of DVB-I. Service discovery is therefore a critical aspect of DVB-I which was first defined in 2019 and updated in 2020. Service discovery is a technical, commercial and legal problem all of which are addressed in the DVB-I Service Discovery and Programmed Metadata standard which provides ways in which clients can access Service Lists and Service List Registries.
Another important aspect of delivery is targetted advertising since advertising underpins the business model of many broadcasters. DVB-TA defines targetted advertising for linear TV and is now being updated to include DVB-I. With DVB-TA, adverts are delivered to the receiver/device over IP based on various criteria and then triggered at the appropriate time as specified by the A178-1 signalling spec.
Ahead of the Q&A, Peter MacAvock introduces the HbbTV organisation explaining how and why it works closely with DVB to generate specifications that drive Hybrid TV forward. Also a member organisation, HbbTV and DVB share many interests but where the DVB’s remit within broadcast is wider than the device-centric HbbTV scope, HbbTV also has a wider scope than DVB since STBs and other devices are in use outside of broadcasting, for instance in retail. Importantly, HbbTV has replaced MHP as DVB’s hybrid TV solution. DVB and HbbTV are sharing the task of making DVB-DASH content and validation tools available to their members.
The Q&A covers controlling of the quality of delivery, getting around the internet’s different reliability compared to RF. They also address scalability with reference to DVB-ABR Multicast. There’s a question on avoiding illegal channels being included in service lists which both Peters acknowledge is a conversation ‘in progress’ for which the technical means exist, but speficially how to implement them is still in discussion a lot of which surrounds ways to establish trust between the device and the service list registars.
The Q&A finishes by discussing whether telcos/ISPs are interested in adopting DVB-ABR Muilticast, compatability between DVB-I and HbbTV as well as 5G broadcast mode.
Watch now!
Download the DVB-I Presentation
Download the HbbTV Presentation
Speakers
 |
Peter MacAvock DVB Chairman Head of Delivery, Platforms and Services, EBU Technology and Development |
 |
Peter Lanigan Senior Manager, Standardisation, TP Vision |
 |
Moderator: Jörn Krieger Freelance Journalist |